Wires suspended above our streets are a late 19th century technology stubbornly persisting into the 21st century. They can hum in a breeze. A wire disturbs the air flow by shedding eddies alternately up and down, sometimes fast enough to be heard as a musical note. The wire’s vibration can enhance the sound’s volume and persistence.
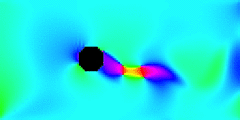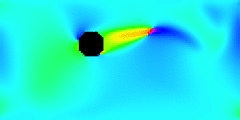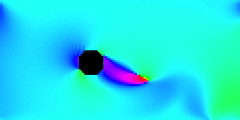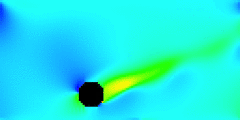

The animation above shows a section of a wire shedding vortices and oscillating transversely to the wind. Saturation indicates wind speed (with white least), and hues indicate wind direction (with cyan rightward), like the polar plot legend. The simulation is an example of desktop computational fluid dynamics, a trans-generational collaboration between the senior thesis of Danielle Shepherd’14 and the junior thesis of Dylan Hamilton’17. Until recently, such simulations have required supercomputers.

Thanks, Mark! I enjoy reading your posts as well.