The motion of one of the simplest dynamical systems, a torqued, damped, nonlinear pendulum, can be infinitely complicated.
Consider a simple pendulum of length l and mass m at a counter-clockwise angle \theta from downward at time t rigidly connected to an axle of radius r wrapped by a rope that hangs down one side with a mass M climbing up and down it, as in the attached animation.
If the climber’s position varies sinusoidally
s = s_0 + A \sin \omega trelative to the hanging rope, then its downward position
y = s + r \thetaand its acceleration
\ddot y = \ddot s + r \ddot \theta = -\omega^2 A \sin \omega t + r \ddot \theta.The total downward force on the climber
M\ddot y = \sum_\text{down} f = Mg-Timplies upper rope tension
T = Mg-M \ddot y = M g + M\omega^2 A \sin \omega t-M r \ddot \theta.If the axle and rope have negligible inertia, then the total torque about the axle
m l^2 \ddot \theta = \sum_\text{CCW}\tau = -mgl \sin\theta + rT-\gamma \dot\theta,where \gamma is the axle viscosity. The full motion equation
m l^2 \ddot \theta = – mgl \sin\theta + rMg + rM \omega^2 A \sin \omega t-Mr^2\ddot\theta-\gamma \dot\thetarearranges to
(ml^2+Mr^2)\ddot \theta = -mgl\sin\theta + rMg + rM\omega^2 A \sin \omega t-\gamma \dot\theta.For parameters that describe the animation’s chaotic motion,
\ddot \theta = – \sin\theta + 0.7155 + 0.4 \sin 0.25 t-0.75 \dot\theta.
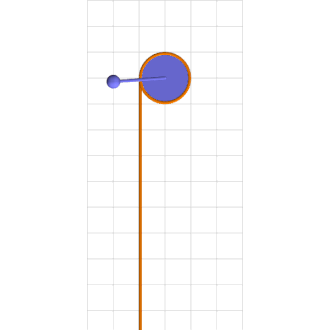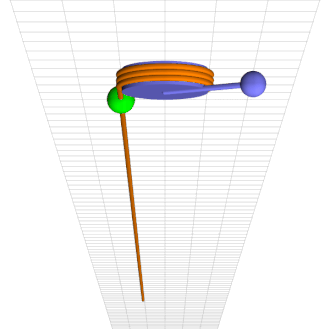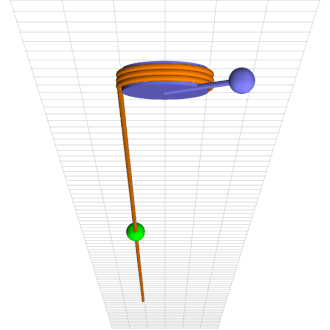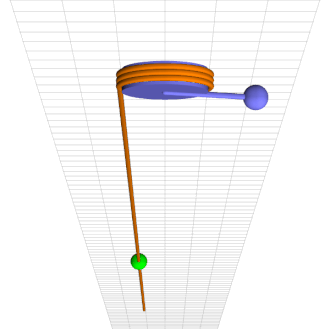
Green mass sinusoidally climbs up and down brown rope torquing blue pendulum into chaotic motion.

Thanks, Mark! I enjoy reading your posts as well.